Science
Related: About this forumTheranostic Nuclear Medicine With Radioactive Isotopes: Looking at the Pictures
The paper to which I'll refer in this post is this one: Theranostic Nuclear Medicine with Gallium-68, Lutetium-177, Copper-64/67, Actinium-225, and Lead-212/203 Radionuclides Focus (Review) Katherine A. Morgan, Stacey E. Rudd, Asif Noor, and Paul S. Donnelly
Chemical Reviews 2023 123 (20), 12004-12035.
"Theranostic" is a term for compounds that serve both as diagnostic tools and treatments. The term suffered some unfortunate associations when the fraudster Elizabeth Holmes named her company "Theranos."
Anyway:
A strategy for addressing cancer that has generated a number of approved drugs is that of the "ADC" or "antibody drug conjugate" where an antibody - a Y shaped protein having a binding site at the tip of the arms known as the CDR (complementarity determining region) which is linked through a chemical "linker" to a "warhead" anticancer drug. The idea is to use the ability of the antibody to recognize a cancer cell's unique receptors to deliver the cancer drug only to the cancer cells as opposed to healthy cells. (Most cancer drugs are cytotoxic and do kill normal cells as well as cancer cells, but exhibit a preference for only killing the latter. By targeting only cancer cells, based on the presence of a receptor unique to them, one can avoid the toxic side efects.)
An interesting modification of this idea is to use instead of a chemical toxin as a "warhead" to attach a radioactive element, complexed to an organic species and a linker to carry it directly to tumor cells.
That is the point of the paper under discussion. In a sense, a real sense, it is inorganic chemistry as an adjunct to biochemistry, as there are organic complexing agents coupled to biomolecules.
It's a review article, and thus rather long, and all I can suggest is to look at the pictures, which follow, but first an excerpt of the introduction:
This paper was published on October 5, 2023. A substance name was corrected in the title, and the paper was reposted on October 10, 2023.
1. Introduction: Personalized Medicine with Radiotheranostics
The term “theranostics” or “theragnostics” describes the use of a diagnostic tool to predict the efficacy of a therapeutic option. (1,2) One approach to use theranostics is to use molecules that selectively target diseased tissue and label them with radionuclides that can be used for either diagnostic imaging or therapy. This radiotheranostic approach is particularly well suited to applications in oncology. (3) The ability to use diagnostic imaging to quantify where a particular drug goes within an individual patient offers the potential for personalized medicine, where patient selection for treatment with targeted radionuclide therapy is determined by the corresponding imaging results. (4) Early clinical applications of radiotheranostics include the use of various isotopes of iodine to diagnose and treat thyroid disorders. (5−7) More recent developments in the ability to target malignancies with molecules that selectively interact with receptors or enzymes overexpressed in cancerous tissue, coupled with the increasing availability of appropriate radionuclides, has reignited interest in radiotheranostics. Several metallic radionuclides have radioactive emissions that are well-suited for either imaging or therapy or even simultaneous imaging and therapy. Innovative advances in manufacturing metallic radionuclides with sufficient purity in economically viable processes and exciting clinical results have led to a surge of interest in radiotheranostics. (3) Ideally, a single molecular agent, called a radiopharmaceutical, could be exploited for both imaging and therapy by using a “matched pair” of isotopes, where one radionuclide is used for imaging and a second radionuclide is used for treatment. (8,9)...
Some pictures:
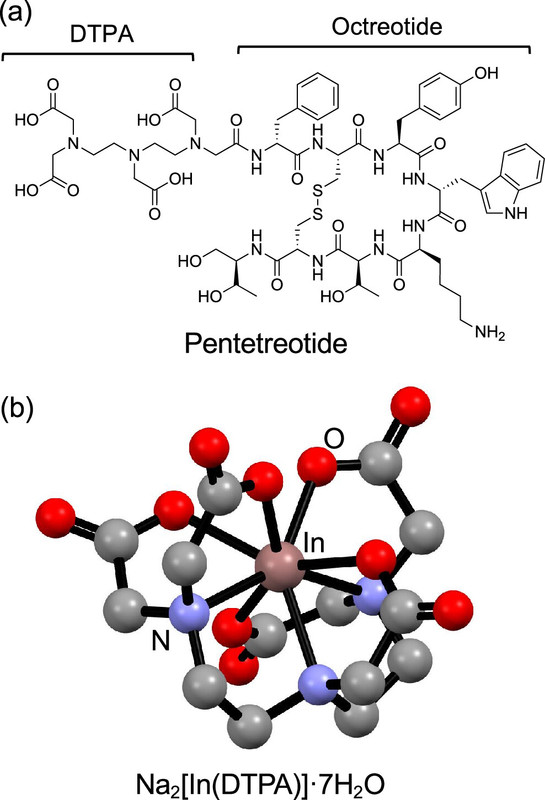
The caption:
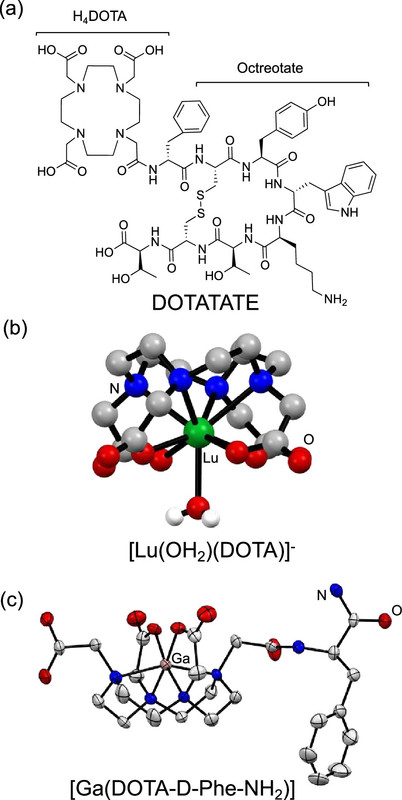
The caption:
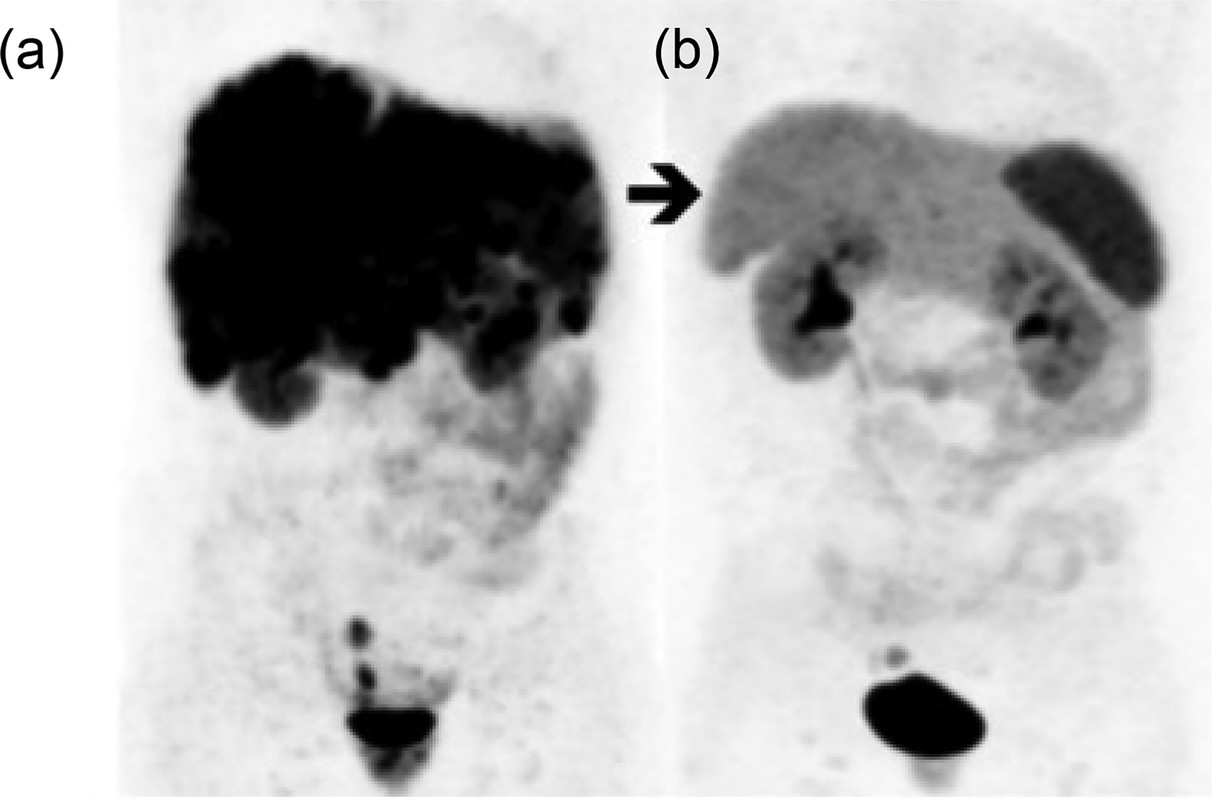
The caption:
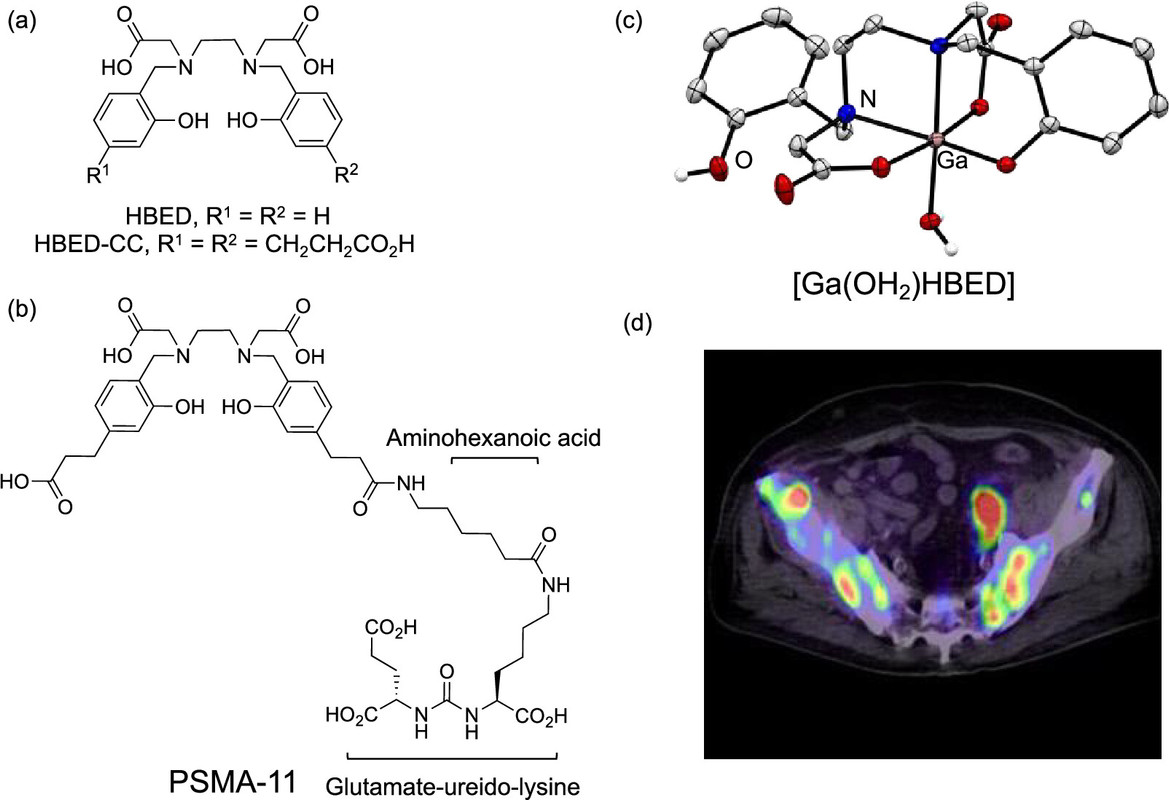
The caption:
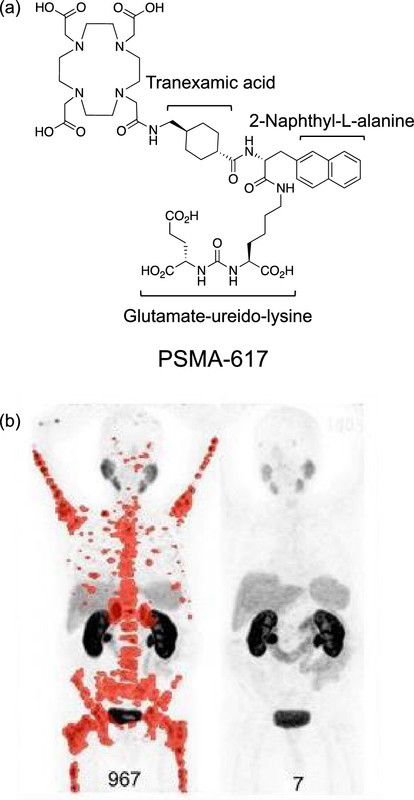
The caption:
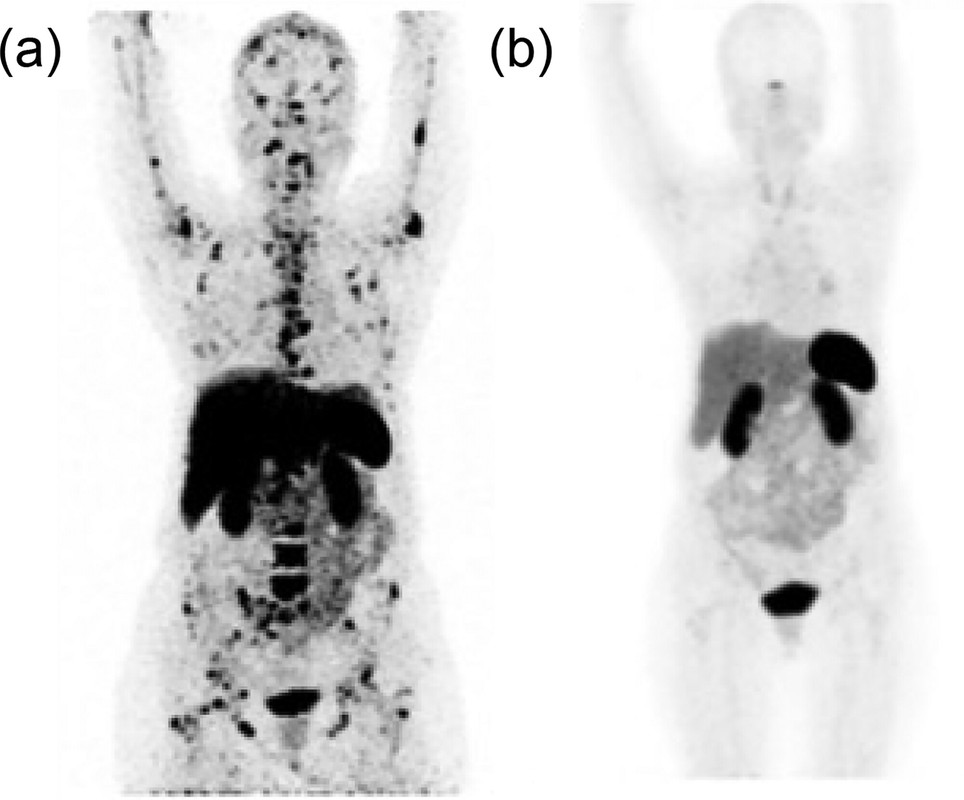
The caption:
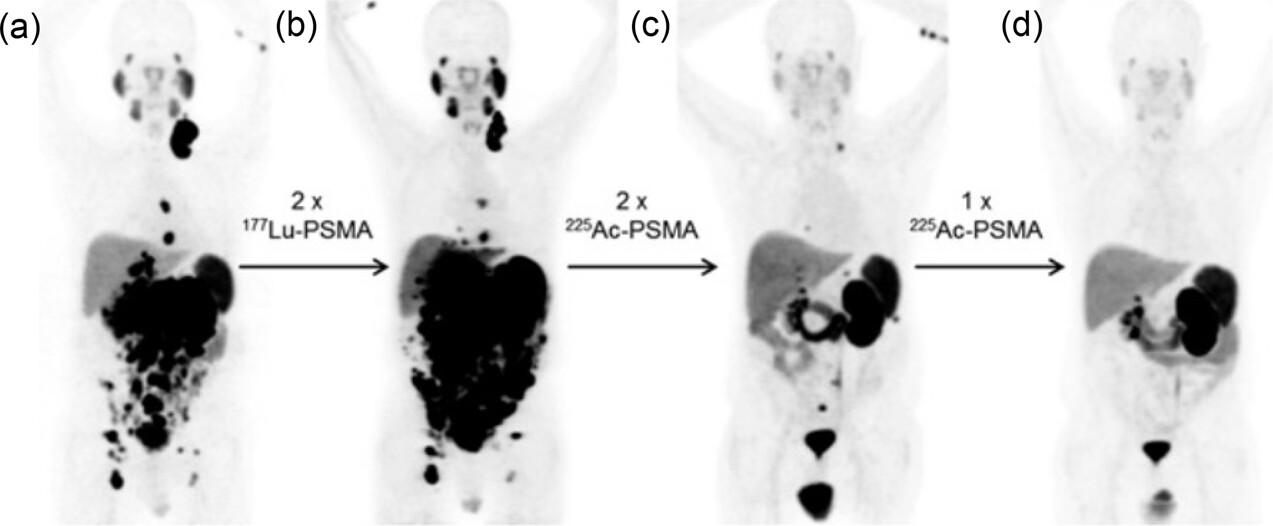
The caption:
Cool stuff I think.
Have a nice week.
Alliepoo
(2,768 posts)It’s very interesting.
Blappy
(157 posts)worked on neuroblastoma under one of the pioneers in the field 15-20 years ago.